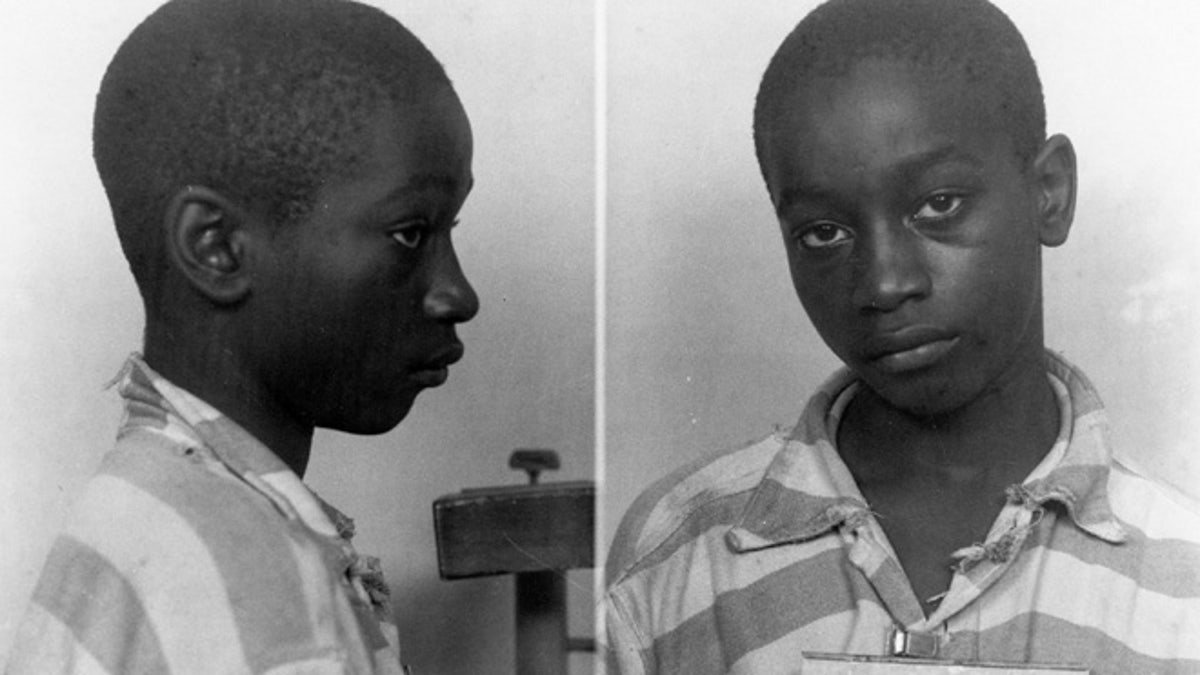
This undated file photo provided by the South Carolina Department of Archives and History shows George Stinney Jr., the youngest person ever executed in South Carolina, in 1944. (AP)
A 14-year-old black boy executed nearly 70 years ago is finally getting another day in court, and his lawyers plan to argue Tuesday for a new trial, saying his conviction was tainted by the segregationist-era justice system and scant evidence.
George Stinney was found guilty in 1944 of killing two white girls, ages 7 and 11. The trial lasted less than a day in the tiny Southern mill town of Alcolu, separated, as most were in those days, by race.
Nearly all the evidence, including a confession that was central to the case against Stinney, has disappeared, along with the transcript of the trial. Lawyers working on behalf of Stinney's family have gathered new evidence, including sworn statements from his relatives accounting for his whereabouts the day the girls were killed and from a pathologist disputing the autopsy findings.
The novel decision of whether to give someone executed a new trial will be in the hands of Circuit Judge Carmen Mullen. Experts say it is a longshot. South Carolina law has a high bar to grant new trials. Also, the legal system in the state before segregation often found defendants guilty with evidence that would be considered scant today. If Mullen finds in favor of Stinney, it could open the door for hundreds of other appeals.
But the Stinney case is unique. At 14, he's the youngest person executed in the United States in the past 100 years. Even in 1944, there was an outcry over putting someone so young in the electric chair. Newspaper accounts said the straps in the chair didn't fit around his 95-pound body and an electrode was too big for his leg.
Stinney's supporters said racism, common in the Jim Crow era South, meant deputies in Clarendon County did little investigation after they decided Stinney was the prime suspect. They said he was pulled from his parents and interrogated without a lawyer.
School board member George Frierson heard stories about Stinney growing up in the same mill town he did, and he has spent a decade fighting to get him exonerated. He swallowed hard as he said he hardly slept Monday night.
"Somebody that didn't kill someone is finally getting his day in court," Frierson said.
In 1944, Stinney was likely the only black in the courtroom. On Tuesday, the prosecutor arguing against him will be Ernest "Chip" Finney III, the son of South Carolina's first black chief justice. Finney argued Tuesday there shouldn't be a new trial because the evidence was lost with the passage of time, not destroyed.
"Back in 1944, we should have known better, but we didn't," Finney said.
Finney has said he will conduct an investigation if a new trial is granted, but what that might find is not known. South Carolina did not have a statewide law enforcement unit to help smaller jurisdictions until 1947. Newspaper stories about Stinney's trial offer little clue whether any evidence was introduced beyond the teen's confession and an autopsy report. Some people around Alcolu said bloody clothes were taken from Stinney's home, but never introduced at trial because of his confession. No record of those clothes exists.
Relatives of one of the girls killed, 11-year-old Betty Binnicker, have recently spoke out as well, saying Stinney was known around town as a bully who threatened to fight or kill people who came too close to the grass where he grazed the family cow.
It isn't known if the judge will rule Tuesday, or take time to come to her decision. Stinney's supporters said if the motion for a new trial fails, they will ask the state to pardon him.









































