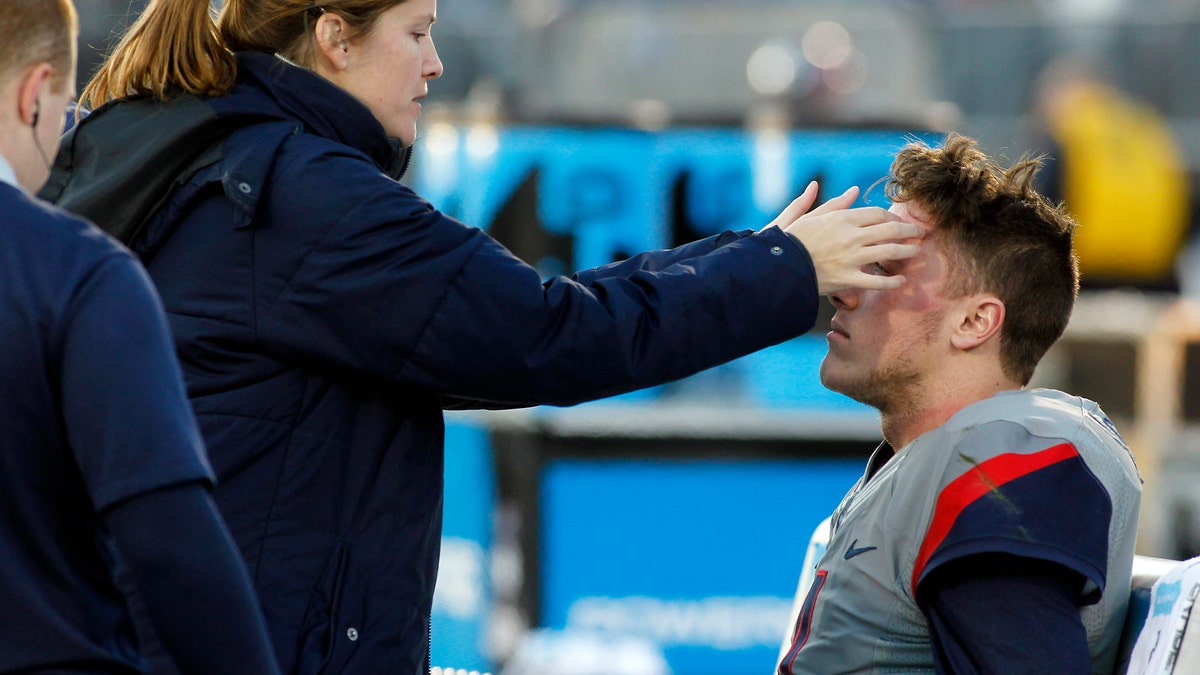
Nov. 21, 2015: In this file photo, medical staff check on Connecticut quarterback Bryant Shirreffs, right, during the first quarter of an NCAA college football game against Houston, in East Hartford, Conn. (AP)
Continuing to play with a concussion may delay athletes from eventually returning to their sport by doing further damage to the brain and lengthening recovery time, a small U.S. study suggests.
Among players in various sports at a National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) Division 1 university, those who continued to play immediately after a concussion averaged an extra five days before being cleared to return to play compared to those who had stopped play immediately after a concussion and reported their symptoms.
Past research has shown that "the brain is likely vulnerable to further physiologic and metabolic changes right after an injury - whether that be from sustaining more impacts or even from continued physical exertion," said lead author Breton Asken, a neuropsychology graduate student in the University of Florida's Clinical Psychology doctoral program.
"Our study relied on a somewhat complicated outcome - being cleared to return to athletic activity - to measure how this physiologic window of vulnerability may express itself clinically," Asken told Reuters Health by email.
Many factors influence when an athlete returns to play, he said. Nonetheless, the study results provide evidence that the "behind the scenes" changes at the level of brain cells that are caused by a concussion may also be compounded or prolonged by playing through a concussion and translate to prolonged recovery, he said.
The researchers analyzed information in the University of Florida Concussion Databank, which collects medical history, details of injury events and assessment data for student athletes. They focused on the 97 athletes, 75 of whom were men, who sustained a concussion during a game or practice between 2008 and 2015.
Athletes who played football, soccer, basketball, swimming, diving, volleyball and other sports were included.
Just over half of the athletes did not report their symptoms and were not immediately removed from play when they sustained a concussion. On average, these players missed more than 13 days of play for recovery compared to about seven days for those who did stop play immediately.
Players whose removal was delayed were also more than twice as likely as players who left the game immediately to have a total recovery time of eight days or more.
In many cases, the researchers could not tell how much longer a player had stayed in the game after suffering a concussion, only that the initial injury had been coded as something other than concussion before the player reported head injury symptoms later, according to the report in the Journal of Athletic Training.
"Our findings indicate that immediately engaging your medical staff if you suspect you have sustained a concussion will give you the best chance to return to your sport more quickly," Asken said.
This message may resonate more with young athletes than the risks of brain injury to their own health, said Dr. Christopher C. Giza of the University of California Los Angeles Brain Injury Research Center, who was not part of the new study.
"For most young people, the threat of a catastrophic occurrence that is very rare isn't great motivation, but getting back in the game quicker, that's something very practical for coaches and athletes," Giza told Reuters Health.
The study did not break down concussion recovery times by individual sport, which could have been useful data, he noted.
"Typically you think about concussions in football and we're starting to think more about it in soccer," but the rules of a sport may make it easier or harder to remove yourself from play immediately, he said. Football includes frequent play stoppages, whereas soccer does not.
Regardless, this study "will be one more tool in my kit where I can tell them here's a good reason to be aware of what the symptoms are, and why it might be important to report symptoms in a teammate," Giza said. "It's not ratting them out, it may be helping them get better faster."