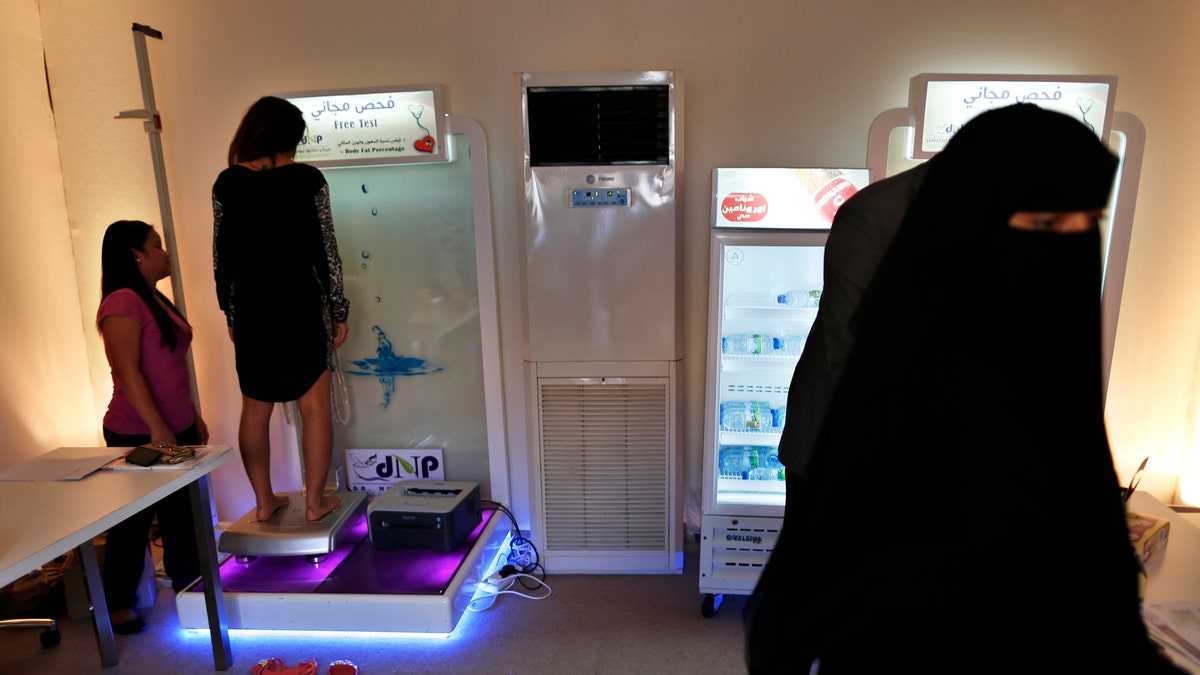
As obesity rates increase among children in the Middle East, some doctors are turning to surgery. Here, a participant weighs in for Dubai's "Your Weight in Gold" challenge, a 30-day weight-loss program launched to fight growing obesity in the Gulf Arab emirate. (REUTERS/Ahmed Jadallah)
RIYADH, Saudi Arabia – Daifailluh al-Bugami was just a year old when his parents noticed that his lips turned blue as he slept at night. It was his weight, doctors said, putting pressure on his delicate airways.
Now Daifailluh is 3, and at 61 pounds he is nearly double the typical weight of a child his age. So the Bugamis are planning the once unthinkable: To have their toddler undergo bariatric surgery to permanently remove part of his stomach in hopes of reducing his appetite and staving off a lifetime of health problems.
That such a young child would be considered for weight-loss surgery—something U.S. surgeons generally won't do—underscores the growing health crisis here and elsewhere in the Middle East. Widespread access to unhealthy foods, coupled with sedentary behavior brought on by wealth and the absence of a dieting and exercise culture, have caused obesity levels in Saudi Arabia and many other Gulf states to approach or even exceed those in Western countries.
While solid national data are hard to come by, some experts say that obesity has turned into a serious health problem for Saudi children, with an estimated 9.3 percent of school-age youths meeting the World Health Organization's body-mass-index criteria for obesity, according to research published in 2013 in the Saudi Journal of Obesity. About 18 percent of school-age children in the U.S. were considered obese in 2010, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Daifailluh's doctor, Aayed Alqahtani, is a leading advocate of a radical approach to the problem. Patients travel to him from across the country and the Gulf region. Over the past seven years, he has performed bariatric surgery on nearly 100 children under the age of 14, which experts on the procedure believe is the largest number performed by one doctor on young children.