Danish immigrant Louis Lassen pioneered the great American hamburger — here’s his sizzling story
Louis Lassen, born in Denmark, was a lunch-wagon owner in New Haven, Connecticut, when he put ground beef patties between two slices of bread. His delicious creation reshaped backyard barbecues and American culinary culture forever.
Americans from sea to shining sea feast on juicy beef burgers dripping with Wisconsin cheddar followed by apple pie or peach cobbler at sun-splashed cookouts each summer.
The more ambitious among us will fuel up for 4th of July road races on Wheaties and fresh-squeezed Florida orange juice.
Every item on that all-American menu has one thing in common.
Not one of them is made from foods native to the United States — or even to the Western Hemisphere.
Beef, cheese, apples, peaches, oranges and even wheat are among hundreds of common, even iconic, American foods foreign to American soil.
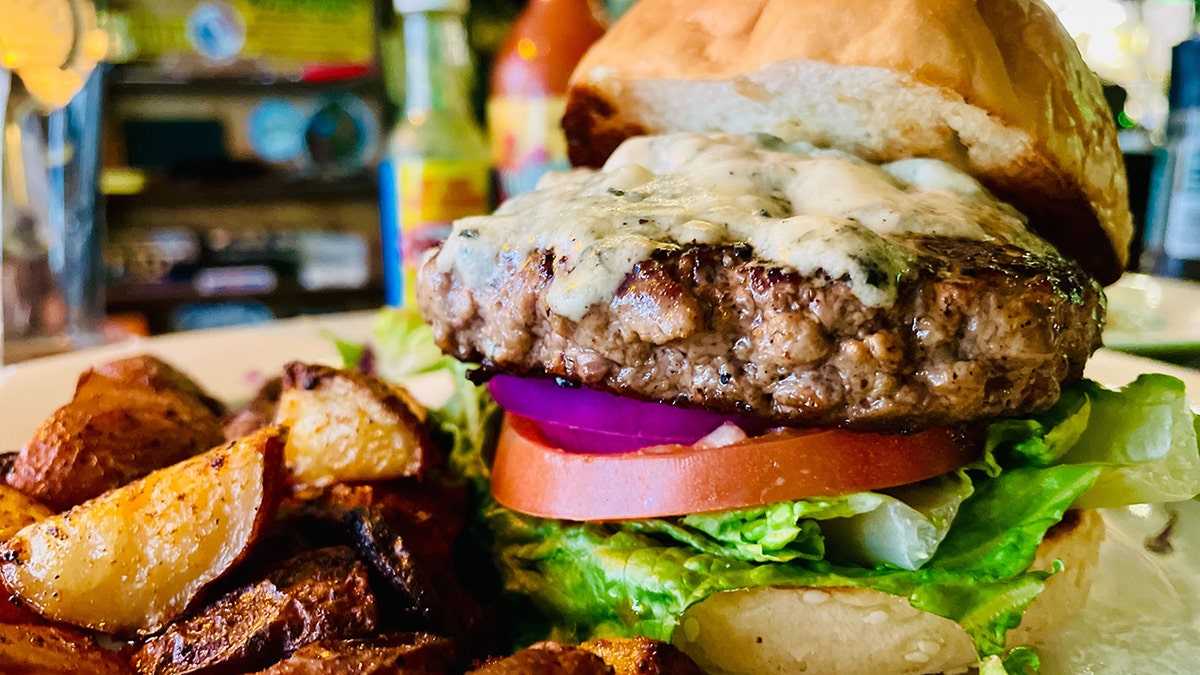

Cheeseburgers are a definitive American food. But neither beef cattle nor dairy cows are native to the Western Hemisphere. They arrived with European explorers in the wake of voyages by Christopher Columbus. (Kerry J. Byrne/Fox News Digital)
Credit a man reviled by academics today: Christopher Columbus.
The Genoese explorer, sailing under the Spanish crown, was much better appreciated by earlier and more enlightened generations.
"Traditional foods of billions of living people are the mute documents of a process set in motion by Columbus."
Columbus inspired global cultural integration more profoundly than any human before or since. He did it all with sextants instead of social-media hashtags touting his devotion to diversity.
"The ostensibly traditional foods of billions of living people are the mute documents of a process set in motion by Columbus," food historian Raymond Sokolov wrote in "Why We Eat What We Eat: How Columbus Changed the Way the World Eats."
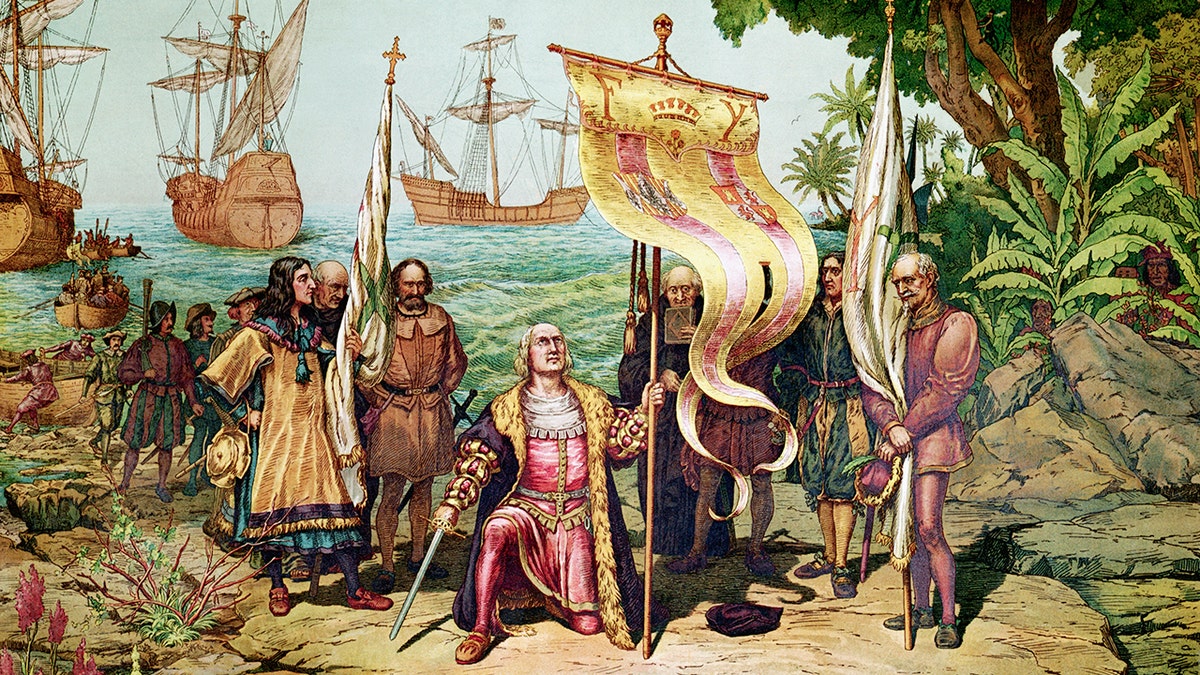

Rendering of Christopher Columbus arriving in the Americas in 1492. Chromo-lithograph by Louis Prang and Company. (Getty Images)
The Columbian Exchange, as its known, went both ways.
Roman emperor Julius Caesar never tasted tomato sauce; Ireland patron St. Patrick never peeled a potato; and French heroine Joan of Arc never cherished chocolate souffle.
MEET THE AMERICAN WHO FIRST PLANTED APPLES IN THE COLONIES: WILLIAM BLAXTON, ECCENTRIC SETTLER
Tomatoes, potatoes and chocolate are all New World natives.
Conversely, many foods we cherish as uniquely American today have surprising worldwide origins.
Here are 10.
1. Apples
Apple pie is the standard by which the American-ness of all things is measured. Johnny Appleseed is treasured as the personification of American bounty.

Apples are considered a barometer of American-ness. But they are native to Central Asia. The first apple orchard in the United States was planted by early settler William Blaxton in the 1630s in Boston, Massachusetts. (iStock)
Apples, however, are native to Central Asia. The Pilgrims themselves celebrated the first Thanksgiving in 1621 without apple pie.
The first apple trees were planted 10 years later in Boston by William Blaxton, the city's first settler.
APPLES VS. ORANGES: WHICH OF THESE FRUITS IS ‘BETTER’ FOR YOU?
The Roxbury russet, possibly descended from Blaxton's original orchard, and named for a Boston neighborhood, is the oldest varietal in the U.S. today.
2, 3, 4. Butter, cheese, milk
Imagine the Land of Milk & Honey without either.
That was the Americas before Columbus. No delicious metaphor to address your sweet love, no way to taunt the greasy-fingered player who drops the ball.
"There were no dairy products, no milk, no cream, no butter, no cheese (before European exploration)."
No way to celebrate victory at the Brickyard on Memorial Day weekend.
The winner of the Indianapolis 500 celebrates his triumph each year by drinking, and often dousing himself, with milk handed to him by an Indiana dairy farmer.
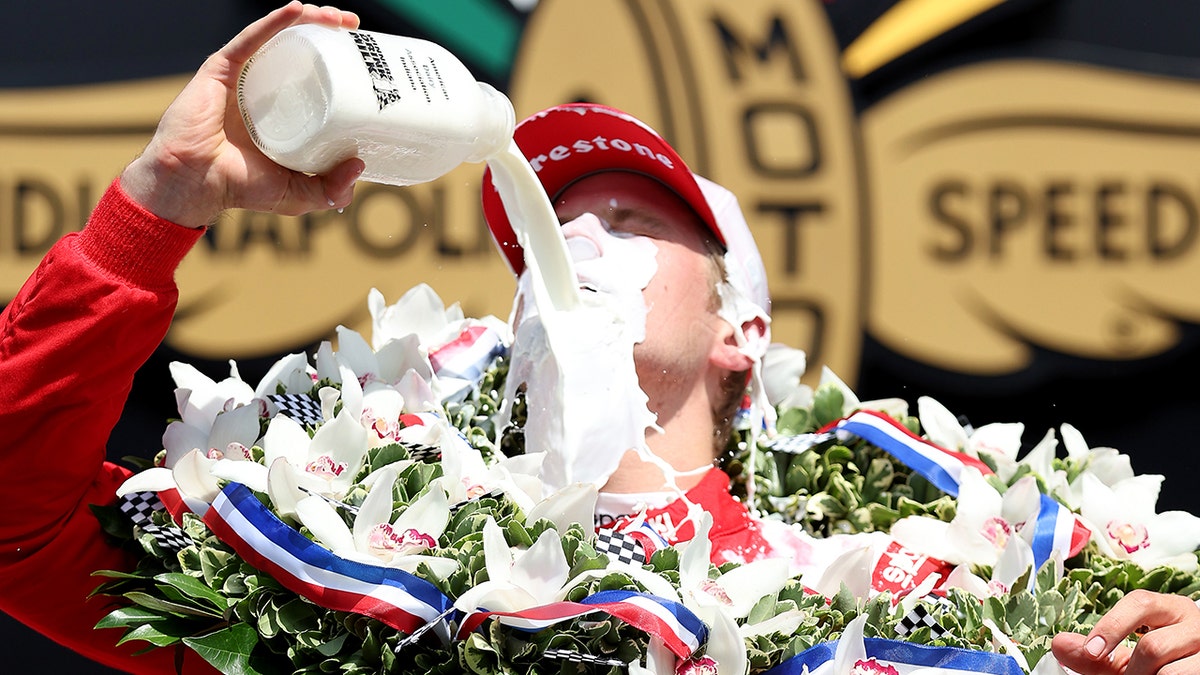

Marcus Ericsson of Sweden celebrates in Victory Lane by pouring milk on his head after winning the 106th Running of The Indianapolis 500 at Indianapolis Motor Speedway in Indianapolis, Indiana, May 29, 2022. (Jamie Squire/Getty Images)
"There were no dairy products, no milk, no cream, no butter, no cheese," before European exploration, writes Sokolov.
Dairy cows and domesticated livestock arrived only with European exploration. Honey bees, too, are an Old World import.
5, 6, 7. Bacon, barbecue, burgers
Sizzling bacon, smoky pork, beef brisket, and cheddar-coated cheeseburgers form a holy alliance of all-American deliciousness.
But pork and beef are both global imports that followed trans-Atlantic trade. That's right: New York sirloin, Texas beef ribs and Carolina pulled pork are culturally appropriated.
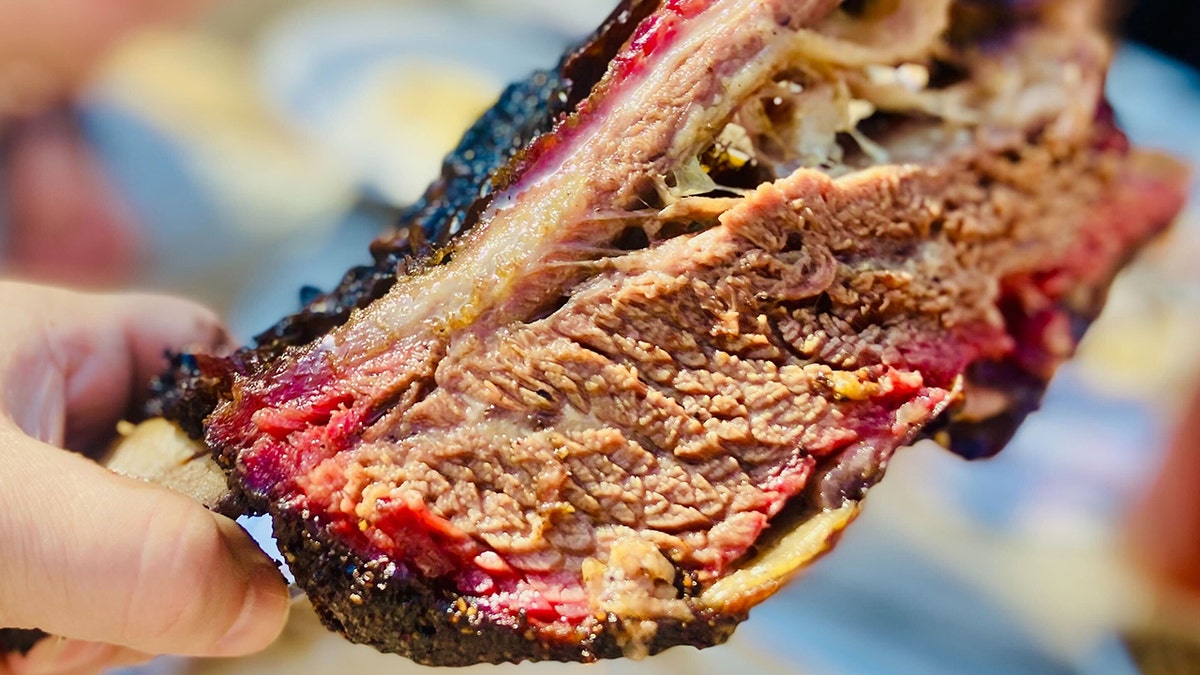

A giant smoky barbecue beef rib from Pecan Lodge in Dallas, Texas. Beef livestock are not native to the Americas. Cattle — and red meat — arrived with European explorers in the 15th and 16th centuries. (Kerry J. Byrne/Fox News Digital)
"Red meat from domestic livestock [was] unknown in Mexico before the Spanish imported (it) … Before 1492, Mexican cuisine had no dishes with beef, pork or lamb."
The livestock prospered and spread across what's now the United States.
They gave us cattle drives, cowboys and John Wayne westerns.
8. Oranges
The U.S. boasts the Orange State, the Orange Bowl and several Orange counties.
But it had no oranges before Columbus.
The sunny citrus fruit, symbolic of both California and Florida, is native to Southeast Asia.
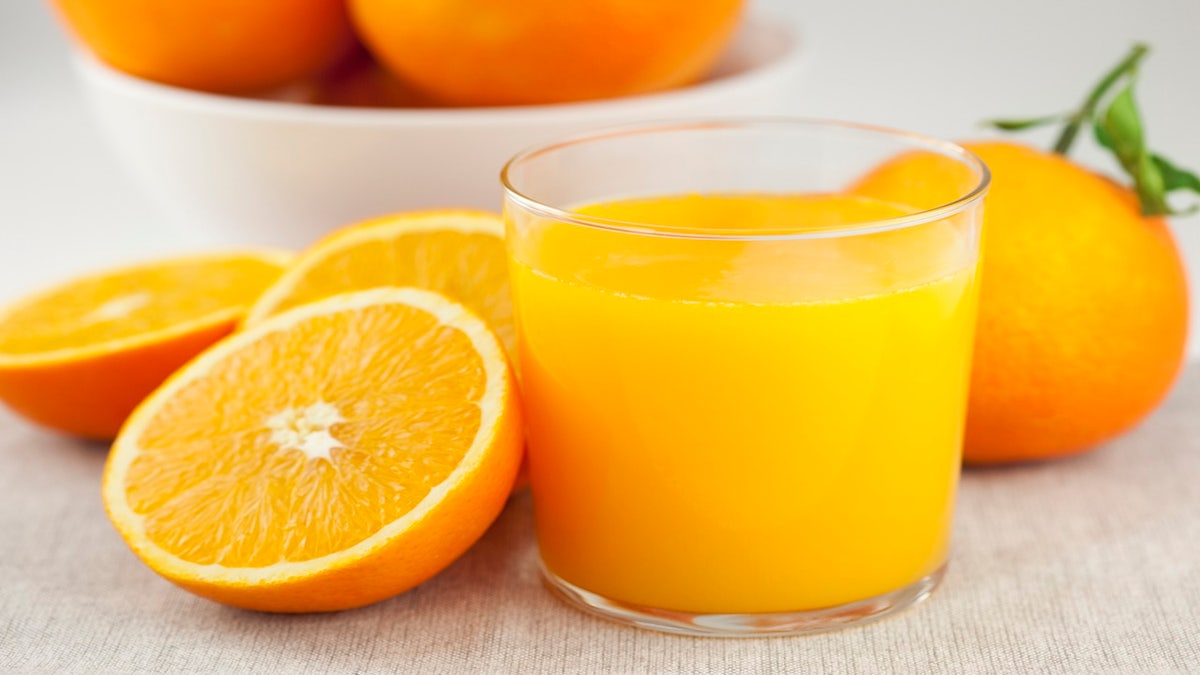

Oranges are signature cash crops for both California and Florida. But oranges are not native to the Western Hemisphere. They arrived in the wake of the Christopher Columbus explorations. (iStock courtesy of contributor CactuSoup)
The fruit was delivered to the New World by Columbus himself during a subsequent voyage in 1493.
"Soon afterward, the Spanish brought citrus to Florida," reports the Florida Division of Historical Resources. "Florida Indians obtained seeds from Spanish missionaries and helped establish the growth of the fruit."
9. Peaches
Atlanta would be a maze of unnamed streets today, Georgia would be best known as the land of a second-rate fiddle-playing devil, and "Reunited" would have been a 1970s solo hit by Herb, without Columbus.
MEET THE AMERICAN WHO INVENTED SLICED BREAD: OTTO ROHWEDDER, HARD-LUCK HAWKEYE
Peaches are native to China, but took a fancy to American soil.
Thomas Jefferson found peaches peachy — and grew dozens of varieties at Monticello, his hilltop Virginia farmstead.
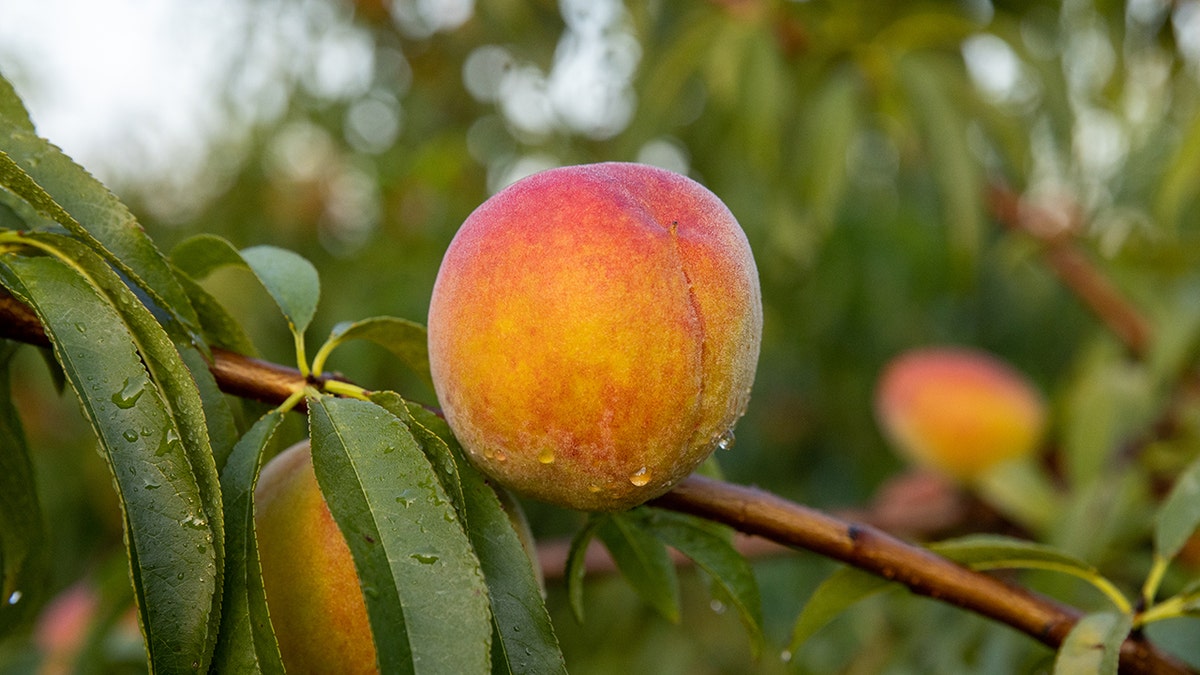

Peaches grow at an orchard in Reynolds, Georgia, on Friday, July 8, 2022. Despite their ubiquitous association with the state, peaches are no longer Georgia's biggest fruit crop. (Dustin Chambers/Bloomberg via Getty Images)
"The peach was introduced either by the Spanish settlers in St. Augustine, Florida, in 1565 or by the French to an isolated Gulf of Mexico settlement in 1562," reports the Monticello website.
"It was probably grown in Mexico at an even earlier date."
10. Wheat (and the Breakfast of Champions)
Wheaties, dubbed the "Breakfast of Champions," has provided a forum to celebrate great American athletes for nearly a century (tennis legend Billie Jean King is the latest).
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR LIFESTYLE NEWSLETTER
The General Mills cereal, and the amber waves of grain used to make it, are coincidental American culinary icons.
Wheaties were discovered in 1921 as a "result of an accidental spill of a wheat bran mixture into a hot stove," General Mills reports on its website.

Tennis legend Billie Jean King is a 39-time Grand Slam champion and an equal rights champion. She is appearing on limited-edition boxes of Wheaties, dubbed "the Breakfast of Champions," starting May 2024. (General Mills via AP)
Wheat was a staple of the Spanish diet.
It flourished in the Americas, first in Mexico and spreading north.
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
The grain was "planted wherever the conquistadors established farms," writes Sokolov.
"By 1535, Mexico was exporting wheat to the Antilles."
For more Lifestyle articles, visit www.foxnews.com/lifestyle.