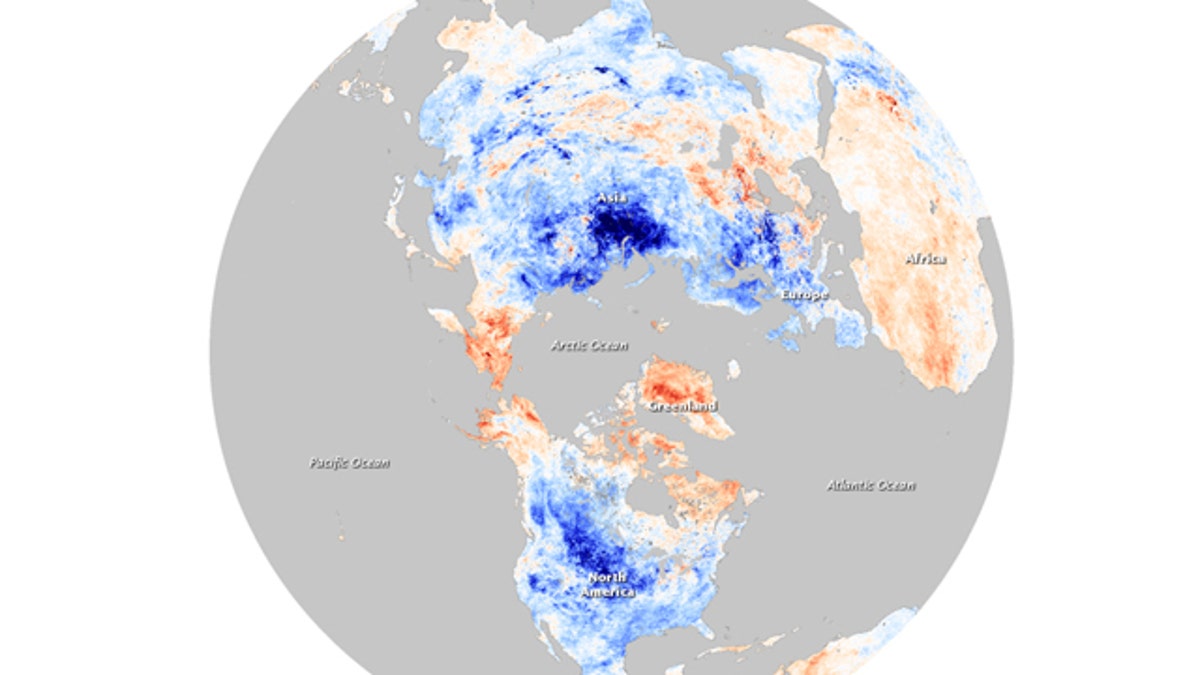
December temperatures compared to average December temps recorded between 2000 and 2008. Blue points to colder than average land surface temperatures, while red indicates warmer temperatures. (NASA Earth Observatory)
From Miami to Maine, Savannah to Seattle, America is caught in an icy grip that one of the U.N.'s top global warming proponents says could mark the beginning of a mini ice age.
Oranges are freezing and millions of tropical fish are dying in Florida, and it could be just the beginning of a decades-long deep freeze, says Professor Mojib Latif, one of the world's leading climate modelers.
Latif thinks the cold snap Americans have been suffering through is only the beginning. He says we're in for 30 years of cooler temperatures -- a mini ice age, he calls it, basing his theory on an analysis of natural cycles in water temperatures in the world's oceans.
Latif, a professor at the Leibniz Institute at Germany's Kiel University and an author of the U.N.'s Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) report, believes the lengthy cold weather is merely a pause -- a 30-years-long blip -- in the larger cycle of global warming, which postulates that temperatures will rise rapidly over the coming years.
At a U.N. conference in September, Latif said that changes in ocean currents known as the North Atlantic Oscillation could dominate over manmade global warming for the next few decades. Latif said the fluctuations in these currents could also be responsible for much of the rise in global temperatures seen over the past 30 years.
Latif is a key member of the UN's climate research arm, which has long promoted the concept of global warming. He told the Daily Mail that "a significant share of the warming we saw from 1980 to 2000 and at earlier periods in the 20th Century was due to these cycles -- perhaps as much as 50 percent."
The U.S. National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSICD) agrees that the cold temperatures are unusual, and that the world's oceans may play a part in temperatures on land.
"Has ocean variability contributed to variations in surface temperature? Absolutely, no one's denying that," said Mark Serreze, senior research scientist with NSIDC. But the Center disagrees with Latif's conclusions, instead arguing that the cold snap is still another sign of global warming.
"We are indeed starting to see the effects of the rise in greenhouse gases," he said.
Many parts of the world have been suffering through record-setting snowfalls and arctic temperatures. The Midwest saw wind chills as low as 49 degrees below zero last week, while Europe saw snows so heavy that Eurostar train service and air travel were canceled across much of the continent. In Asia, Beijing was hit by its heaviest snowfall in 60 years.
And as for the cold weather?
"This is just the roll of the dice, the natural variability inherent to the system," explained Serreze.
Editor's note: An earlier version of this article erroneously reported that the NSIDC reports concluded that the warming of the Earth since 1900 is due to natural oceanic cycles.








































