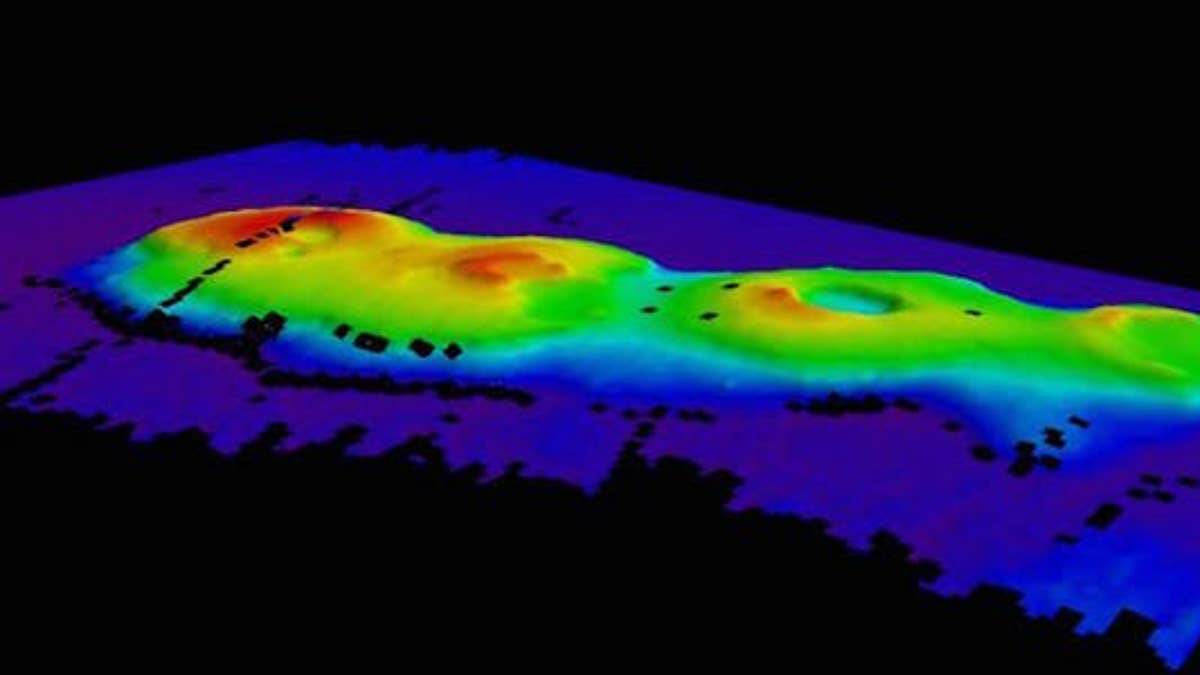
During a mission to find larval lobsters, marine researchers unexpectedly found a cluster of extinct, 50-million-year-old volcanoes on the ocean floor near eastern Australia. (Marine National Facility)
During a recent marine excursion, researchers searching for lobster larva unexpectedly discovered a geologic wonder: a 50-million-year-old cluster of extinct volcanoes submerged in the water off eastern Australia.
The four volcanoes are located about 155 miles off the coast of Sydney, the researchers found during the mission, which lasted from June 3 to 18. The scientists immediately recognized them as calderas, a cauldronlike structure that forms after a volcano erupts and collapses into itself, creating a crater. The largest extinct volcano measures about 1 mile across and towers about 0.4 miles above the seafloor, the researchers said.
The cluster is a large one, measuring about 12 miles long and 4 miles wide, they added. [Axial Seamount: Images of an Erupting Undersea Volcano]
The discovery will help geoscientists learn more about the geological forces that shaped the region, said Richard Arculus, a professor of marine geology at the Australian National University and an expert on volcanoes.
"They tell us part of the story of how New Zealand and Australia separated around 40 [million to] 80 million years ago, and they'll now help scientists target future exploration of the seafloor to unlock the secrets of the Earth's crust," Arculus said in a statement.
The volcano cluster, which sits about 3 miles underwater, went unnoticed until now because researchers didn't have adequate tools to measure and map the deep seafloor, Arculus said.
The sonar on the old research vessel run by Marine National Facility (MNF), a research group funded by the Australian government, only had the ability to map the seafloor to about 1.9 miles underwater, he said. A new 308-foot-long vessel, named the Investigator, has a greater scope.
"On board the new MNF vessel, Investigator, we have sonar that can map the seafloor to any depth, so all of Australia's vast ocean territory is now within reach, and that is enormously exciting," Arculus said.
During the Investigator's latest mission, researchers were looking for the nursery grounds of lobster larvae while simultaneously carrying out a routine mapping of the seafloor.
"The voyage was enormously successful," Iain Suthers, a professor of marine biology at the University of New South Wales, said in the statement. "Not only did we discover a cluster of volcanoes on Sydney's doorstep, we were amazed to find that an eddy off Sydney was a hotspot for lobster larvae at a time of the year when we were not expecting them."
During the mission, the Investigator's crew sent data to a team at the University of New South Wales, who analyzed the information and sent back their results, which included satellite imagery. This allowed the marine crew to chase eddies created by the marine creatures they were tracking.
"This is the first time we've been able to respond directly to the changing dynamics of the ocean and, for a biological oceanographer like me, it doesn't get more thrilling," Suthers said.
The research team found juvenile fish popular among fishermen, such as bream and tailor, about 93 miles offshore.
"We had thought that once they were swept out to sea, that was [the] end of them," Suthers said. "But, in fact, these eddies are nursery grounds along the east coast of Australia."
- In Photos: New Seamount Discovered Beneath Pacific Ocean
- Photos: Hawaii's New Underwater Volcano
- The 10 Biggest Volcanic Eruptions in History
Copyright 2015 LiveScience, a Purch company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.








































