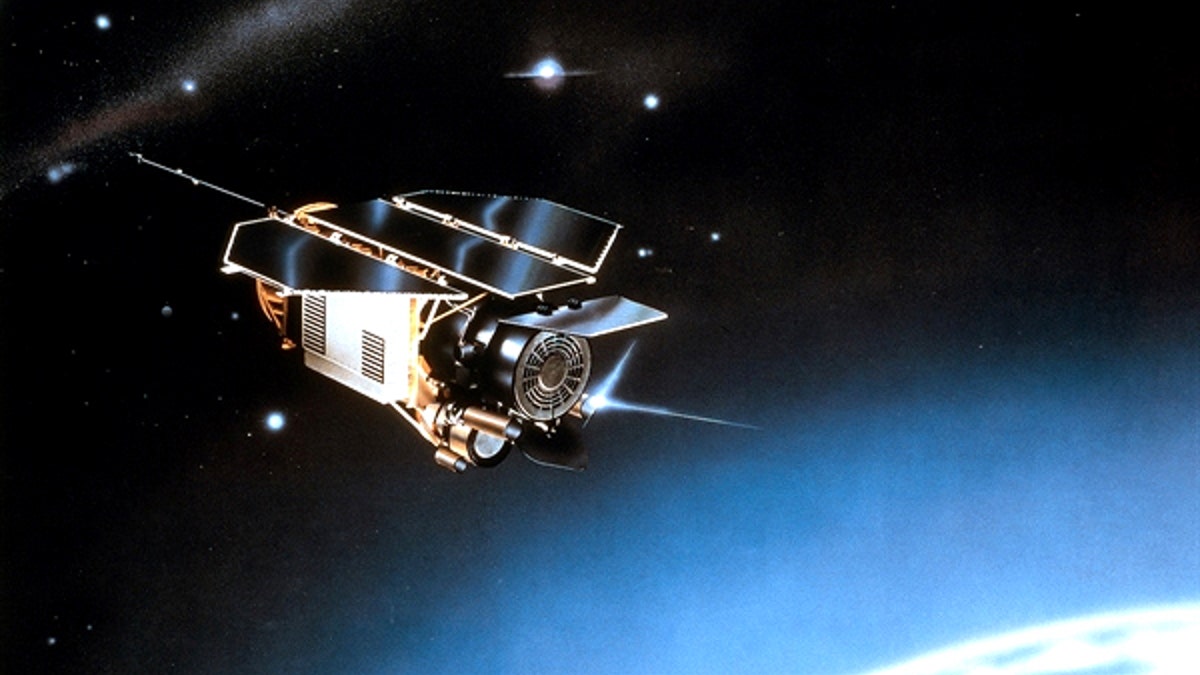
An artist's impression of the German ROSAT satellite orbiting in space. (German Aerospace Center)
A defunct satellite entered the atmosphere early Sunday and pieces of it were expected to crash into the earth, the German Aerospace Center said.
There was no immediate solid evidence to determine above which continent or country the ROSAT scientific research satellite entered the atmosphere, agency spokesman Andreas Schuetz said.
The 2.7-ton Roentgen Satellite, or ROSAT, will likely plummet to Earth on Saturday or Sunday (Oct. 22 or 23), according to the German Aerospace Center.
"Currently, the re-entry date can only be calculated to within plus/minus one day," agency officials said in a statement. "This time slot of uncertainty will be reduced as the date of re-entry approaches. However, even one day before re-entry, the estimate will only be accurate to within plus/minus five hours."
Track the falling ROSAT satellite in real-time
ROSAT weighs about 5,348 pounds (2,426 kilograms) and launched into orbit in June 1990 as part of a joint mission by Germany, the United States and the United Kingdom. In 1998, the satellite's star tracker failed, which caused its X-ray sensors to point directly at the sun. This permanently damaged the spacecraft, and ROSAT was officially decommissioned in February 1999. [Photos of Doomed ROSAT Satellite]
The falling German satellite's impending plunge through the atmosphere comes about a month after an old NASA climate satellite also fell uncontrolled to Earth, in what was a much publicized event. The Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite (UARS) splashed into the Pacific Ocean, well away from the North American coastline, on Sept. 24.
The ROSAT spacecraft is smaller than the UARS satellite, which was about the size of a school bus and weighed about 6 1/2 tons. Still, German space officials expect ROSAT to drop debris along a 50-mile (80-km) stretch of the Earth's surface.
The satellite's orbit reaches from the latitudes of 53 degrees north and south, which means ROSAT could fall anywhere in an area stretching from Canada to South America. While officials have stated that there is a 1-in-2,000 chance that a piece of ROSAT could strike someone somewhere on Earth, the odds of any debris landing in a densely populated area are remote.
Germany's X-ray ROSAT observatory is expected to break up as it falls to Earth, but some large pieces are expected to survive the intense heat of re-entry. Up to 30 pieces of debris, totaling 1.9 tons (1.7 metric tons), could reach the Earth's surface, German aerospace officials said. These fragments will likely be pieces of the satellite's heat resistant mirrors and ceramic parts.
Mission controllers are actively tracking the satellite as its orbit gradually decays, but officials will not be able to make more precise determinations of when and where the satellite will fall until a few hours before ROSAT impacts the Earth.
* 6 Biggest Spacecraft to Fall Uncontrolled From Space
* The Facts About Germany's Falling Satellite ROSAT (Infographic)
* The Falling German Satellite ROSAT: Biggest Questions & Answers
Copyright 2011 Space, a TechMediaNetwork company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.
The Associated Press contributed to this report.
