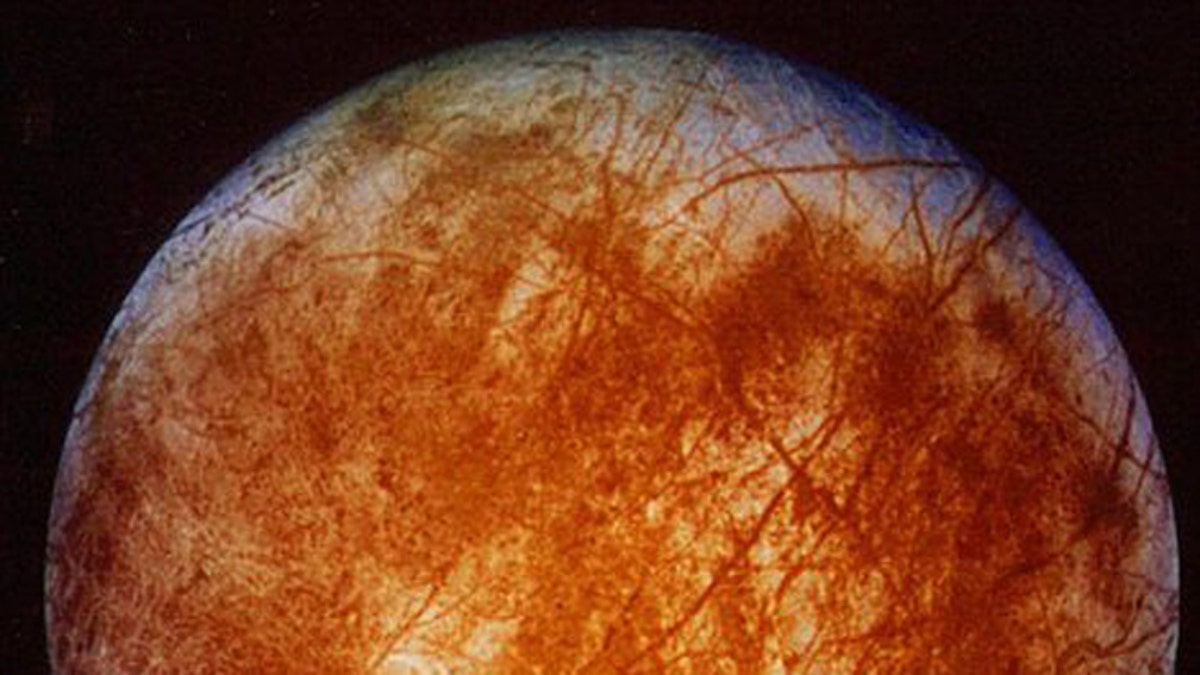
Jupiter's moon Europa is thought to have a metallic core surrounded by a rocky interior, and then a global ocean on top of that, surrounded by a shell of water ice. (AP)
The ocean underneath the icy shell of Jupiter's moon Europa might be too acidic to support life, due to compounds that may regularly migrate downward from its surface, researchers say.
Scientists believe that Europa, which is roughly the size of Earth's moon, possesses an ocean perhaps 100 miles deep (160 kilometers). This ocean is overlain by an icy crust of unknown thickness, although some estimates are that it could be only a few miles thick.
Since there is life virtually wherever there is liquid water on Earth, for many years scientists have entertained the notion that this Jovian moon could support extraterrestrials. Recent findings even suggest its ocean could be loaded with oxygen, enough to support millions of tons worth of marine life like the kinds that exist on Earth.
Researchers have proposed missions to penetrate Europa's outer shell to look for life in its ocean, although others have suggested that Europa could harbor fossils of marine life right on the surface for prospectors to find, given how water apparently regularly gets pushed up from below.
However, chemicals found on the surface of Europa might jeopardize any chances of life evolving there, scientists find. The resulting level of acidity in its ocean "is probably not friendly to life — it ends up messing with things like membrane development, and it could be hard building the large-scale organic polymers," said Matthew Pasek, an astrobiologist at the University of South Florida. [Photos of Jupiter's Moon Europa]
Destructive chemicals
The compounds in question are oxidants, which are capable of receiving electrons from other compounds. These are usually rare in the solar system because of the abundance of chemicals known as reductants such as hydrogen and carbon, which react quickly with oxidants to form oxides such as water and carbon dioxide.
Europa happens to be rich in strong oxidants such as oxygen and hydrogen peroxide, which are created by the irradiation of its icy crust by high-energy particles from Jupiter.
The oxidants on Europa's surface are likely carried downward in potentially substantial quantities by the same churning that causes water to rise from below. Oxidants could be of great use to any life in Europa's ocean — for example, oxygen was pivotal to how complex life evolved on Earth.
However, oxidants from Europa's surface might react with sulfides and other compounds in its ocean before life could nab it, generating sulfuric and other acids, investigators said. If this has occurred for just about half of Europa's lifetime, not only would such a process rob the ocean of life-supporting oxidants, but it could become relatively corrosive, with a pH of about 2.6 — "about the same as your average soft drink," Pasek said.
This level of acidity would be a significant challenge for life, unless organisms were to consume or sequester oxidants fast enough to ameliorate the acidification, researchers said. The ecosystem would need to evolve quickly to meet this crisis, with oxygen metabolisms and acid tolerance developing in only about 50 million years to handle the acidification.
Extremophiles on Europa?
Any surviving ecosystem in Europa's ocean might be analogous to the microbial community found in acid mine drainage on Earth, such as the bright red Río Tinto river in Spain. The dominant microbes found there are acid-loving "acidophiles" that depend on iron and sulfide as sources of metabolic energy.
"The microbes there have figured out ways of fighting their acidic environment," Pasek said. "If life did that on Europa, [Jupiter's moon] Ganymede, and maybe even Mars, that might have been quite advantageous."
Others have questioned whether or not rock in Europa's seabed might actually neutralize the effects of this acidity. Pasek does not think this is likely — even if such minerals were present, there is probably not enough of it exposed to reduce acidity by much, he said.
The calcium-based materials that bones and shells on Earth are made from might dissolve pretty readily in such an acidic environment. However, "one of the interesting possibilities is that they might have used blue phosphates as their bone material instead to evolve large organisms," Pasek said. "If you have iron phosphates, you make a pretty blue mineral called vivianite."
Pasek and co-author Richard Greenberg detailed their findings online Jan. 27 in the journal Astrobiology.
- Target: Jupiter — Missions to the Solar System's Largest Planet
- Touring Jupiter's Big Moons: Io, Ganymede, Europa, Callisto
- Where Europa's Ocean & Ice Meet
Copyright 2012 SPACE.com, a TechMediaNetwork company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.
