How does obesity, smoking factor into coronavirus susceptibility?
How does obesity, smoking factor into coronavirus susceptibility?
Get all the latest news on coronavirus and more delivered daily to your inbox. Sign up here.
African officials warned Thursday that if the coronavirus pandemic is left to spread on the continent, the rest of the world will remain at risk for COVID-19.
“We cannot be neglected in this effort,” the head of the Africa Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, John Nkengasong, told reporters. “The world will be terribly unsafe, and it will be completely naive, if countries think they can control COVID-19 in their countries but not in Africa.”
Equipment such as medical equipment to combat the coronavirus in Africa is scarce. The World Health Organization says fewer than 5,000 intensive care unit beds are available across 43 of the continent’s 54 countries: “This is about 5 beds per 1 million people in the reported countries compared to 4,000 beds per 1 million people in Europe.” Functional ventilators in public health services across 41 countries number less than 2,000, a severe shortage for patients in respiratory distress.
While Africa’s 1.3 billion people had a head start in preparing for the pandemic as the virus spread in China, Europe and the United States, Nkengasong warned that “the very future of the continent will depend on how this matter is handled” as the number of cases, now over 11,000, quickly rise.
“The worst is still to come,” he said, and pointed to the global Spanish flu pandemic of a century ago when cases came in waves.
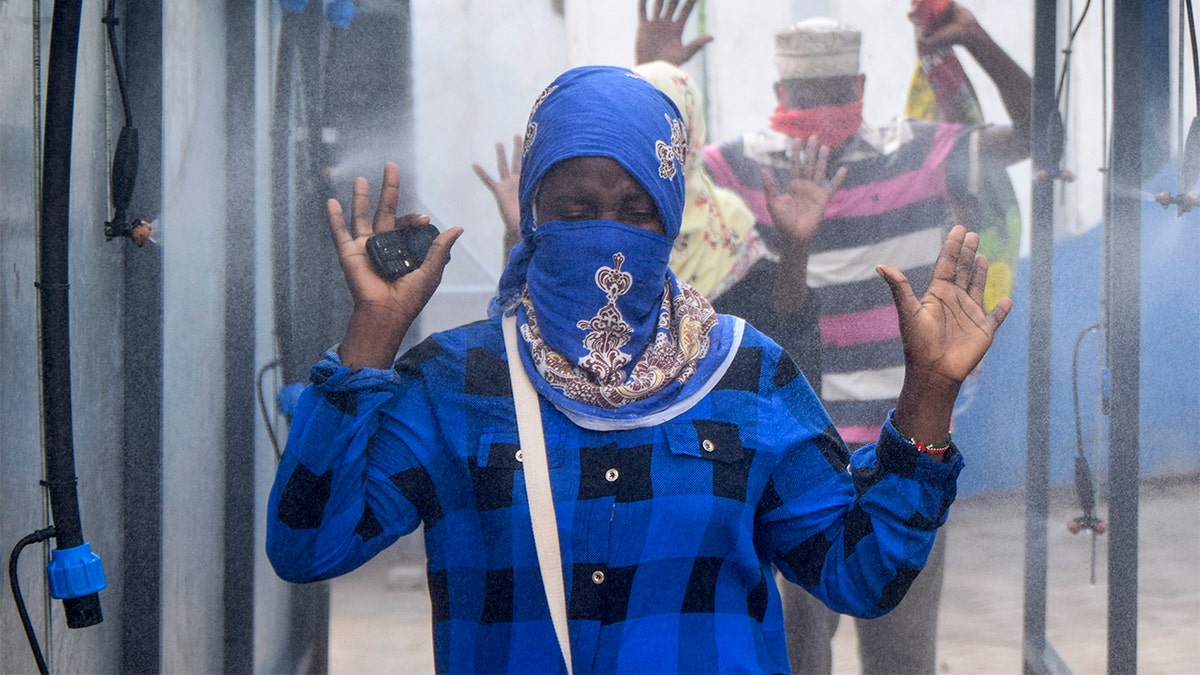

Ferry commuters walk through an automated disinfecting machine installed this week that sprays disinfectant onto all passengers boarding or disembarking ferries that cross the harbor of Mombasa, on the south coast of Kenya Wednesday. (AP Photo)
CLICK HERE FOR COMPLETE CORONAVIRUS COVERAGE
Africa is also competing with the developing world for testing kits that will help give a clear number of cases, as well as protective equipment that front2line health workers desperately require. Already, anxious workers have gone on strike or gone to court in places like Zimbabwe over the lack of gear.
“We may not actually know how big is the size of the problem” without scaling up testing, Nkengasong said.
While 48 of Africa’s 54 countries now have testing capability, that often is limited to countries’ capitals or other major cities, WHO officials told reporters in a separate briefing.
There is an “urgent need” to expand testing, the WHO Africa chief, Matshidiso Moeti, said, noting that clusters of community transmission have emerged in at least 16 countries. That means the virus has begun spreading beyond the initial cases imported from abroad.
“Some countries might face a huge peak very soon” in cases, said the WHO’s emergency program manager, Michel Yao.
Even if testing kits and other equipment are found, another challenge is delivering them amid the thicket of travel restrictions. Cargo space is rare because many airlines have stopped flights to African destinations, Yao said.
Close to 20 African countries have closed their borders, and several are now under lockdown to try to prevent the virus’ spread. Now millions of people are bracing for lockdown extensions after regional leader South Africa’s announcement Thursday night.
The economic toll has been harsh. The World Bank in a new report said sub-Saharan Africa is expected to fall into recession for the first time in a quarter-century. Growth should fall this year from 2.4 percent to minus 2.1 percent, with countries that depend heavily on oil exports and mining hit especially hard.
Africa has had some of the world’s fastest-growing economies. The World Bank said African nations will require a “debt service standstill” and other financial assistance as millions of people, many who survive day-to-day, can’t go out to work.
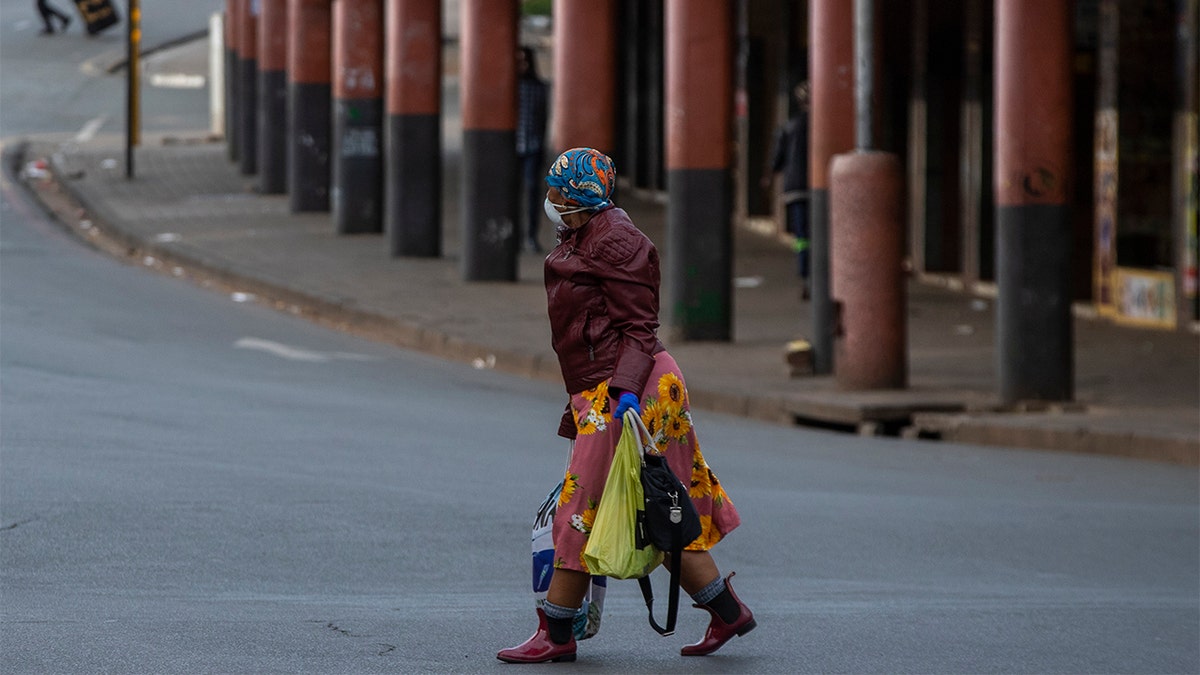

A woman wearing face masks to protect against coronavirus, walks on the street in downtown Johannesburg, South Africa, Thursday. (AP Photo/Themba Hadebe)
CORONAVIRUS: WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
South Africa has the most confirmed cases in Africa with more than 1,900.
“We are only at the beginning of a monumental struggle,” President Cyril Ramaphosa said. “We cannot relax and we cannot be complacent.”
The Associated Press contributed to this report.