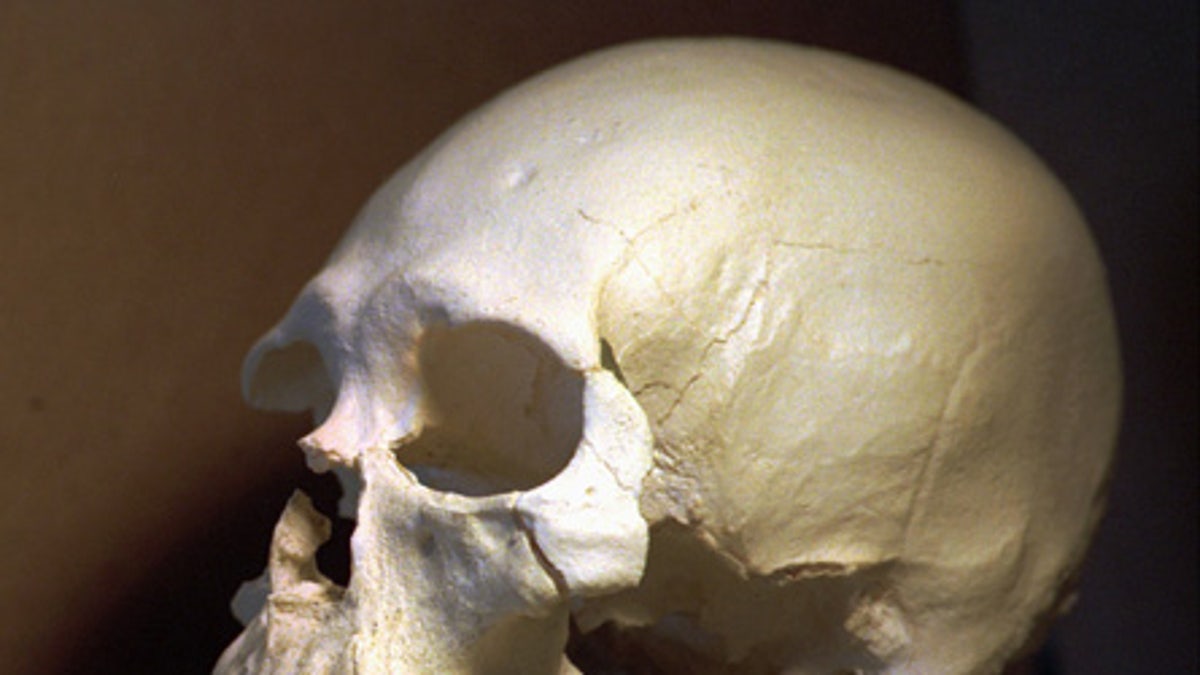
FILE - This July 24, 1997 file photo shows a plastic casting of the skull from the bones known as Kennewick Man in Richland, Wash. The ancient skeleton, found nearly 20 years ago in a river in Washington, is related to Native Americans, says a DNA study published Thursday, June 18, 2015. The finding could help resolve a long-running dispute over its ancestry and custody. (AP Photo/Elaine Thompson, File)
DNA analysis of an 8,500-year-old skeleton found in Washington state 19 years ago says the so-called "Kennewick Man" is related to Native Americans, marking the latest twist in a long-running dispute over its custody.
Most scientists trace modern native groups to Siberian ancestors who arrived by way of a land bridge that used to extend to Alaska. But features of Kennewick Man's skull led some scientists to suggest its ancestors came from elsewhere.
Researchers turned to DNA analysis to try to clarify the skeleton's ancestry. They recovered DNA from a fragment of hand bone, mapped its genetic code and compared that to modern-day DNA from native peoples of the Americas and populations around the world.
The results showed a greater similarity to DNA from the Americas than from anywhere else, with a close relationship to at least one Native American population in Washington.
Some Native American tribes have asked that the skeleton be handed over to them for reburial, under a 1990 federal law aimed at returning certain Native American cultural items, including human remains, to descendants and culturally affiliated tribes. The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, which manages the land where Kennewick Man was found, planned to grant the request. But some scientists sued to block that, saying the bones should be kept available for study.
In 2004, a federal appeals court agreed with lower court decisions to block the handover, agreeing with the scientists that the law did not apply because there was no evidence to connect the remains to any existing tribe.
It's not clear what the results of the DNA analysis will mean for the dispute.
One group that had asked for the remains, the Washington-based Colville tribe, donated DNA for the work. Analysis showed that Kennewick Man is "very closely related to the Colville," said Eske Willerslev of the University of Copenhagen, senior author of the study. He said DNA from the other tribes that had asked for the bones was not available for the study, but that he suspected they are closely related, too.
But he said he and his team took no position on the legal question about custody of the skeleton. The work received no funding from any Native American group, he said. He met with members of the Colville tribe earlier this week to share the results.
Jim Boyd, chairman of the council that governs the Confederated Tribes of the Colville Reservation, said the findings will aid the tribal efforts to rebury the remains.
"We have always maintained the belief that the Ancient One was one of us," he said, using the tribal term for Kennewick Man.
But one of the scientists who sued to block the turnover said he doesn't think the new results connect the skeleton clearly enough to the Colville group to justify handing them over under the federal law.
"The results do not tie Kennewick Man exclusively to the Colville," said Doug Owsley, division head for physical anthropology at the Smithsonian Institution's National Museum of Natural History,
Other data show Kennewick Man was "a traveler.... His people were coming from somewhere else. We don't know who that people (were), we don't know what their culture was," Owsley said.
Willerslev said that because researchers don't have a comprehensive collection of DNA samples from native populations in the Americas, they can't tell what population Kennewick Man is most closely related to.
Brig. Gen. John Kem, commander of the Northwestern Division of the Corps of Engineers, said his staff will analyze the research so he can decide whether to turn the bones over to the tribes. The skeleton is stored at the Burke Museum of Natural History and Culture in Seattle.
Ancient remains have been reburied before after scientific study. Last year, 12,600-year-old bones of a baby boy found in Montana were reburied in a tribal ceremony after DNA showed links to native peoples.
Kennewick Man was uncovered in 1996 after two men stumbled across part of its skull in the Columbia River near the city of Kennewick in southern Washington. The research, by an international team of scientists, was published online Thursday by the journal Nature.
The Associated Press contributed to this report.
